
Electric Cars
Electric cars mark a new chapter in sustainable mobility, combining zero-emission performance with the latest in automotive innovation. KGM’s electric range is powered by advanced motors and high-capacity batteries, delivering an impressive battery range, smooth acceleration, and quiet, refined driving.
With rapid charging capabilities, KGM electric cars make every journey easier and more flexible, helping you recharge quickly and travel further with fewer stops. Intelligent energy management systems also help maximise efficiency and performance on every drive, whether it’s a short commute or a trip covering long distances.
Electric cars also offer significant advantages when it comes to running costs and maintenance, helping drivers save money while reducing their environmental impact.
Want to learn more about electric vehicles? Visit our FAQs section at the end of this page for answers to common questions about EVs.
Ready to make the switch? Explore the KGM electric range and discover your next EV.
Torres EVX
Mid-Size Electric SUV
The KGM Torres EVX is an electric SUV built to make switching to electric driving easy and exciting. It delivers the power, space, and practicality of a traditional SUV, but with the smooth, quiet performance and zero-emissions benefits of an electric car.
Powered by an advanced electric powertrain and a 73.4 kWh battery, the Torres EVX offers an impressive electric car range of up to 287 miles (WLTP), so you can take on daily commutes or long journeys with confidence. Thanks to fast-charging capability, you can recharge at public charging points quickly and get back on the road in no time, with minimal charging time and plenty of flexibility.
Driving feels effortless, with instant acceleration and a refined, responsive driving experience that adapts to your driving style. Lower running costs, zero road tax, and no tailpipe emissions make the Torres EVX a smart choice for drivers ready to make the move to electric.
Step inside, and the clean, modern interior feels both high-tech and practical. Dual 12.3-inch digital displays, Apple CarPlay and Android Auto, and smart storage throughout the cabin make every journey feel comfortable and connected. With a generous 703 litres of boot space, there’s room for everything you need for everyday life or weekend adventures.
The Torres EVX is packed with advanced safety and driver-assist features, and it’s backed by KGM’s 7-year/90,000 mile warranty for complete peace of mind.
With its bold design, long range, and real-world practicality, the KGM Torres EVX proves that switching to electric doesn’t mean compromising on capability. It’s ready for you to experience, so why not book a test drive and see what makes it different?
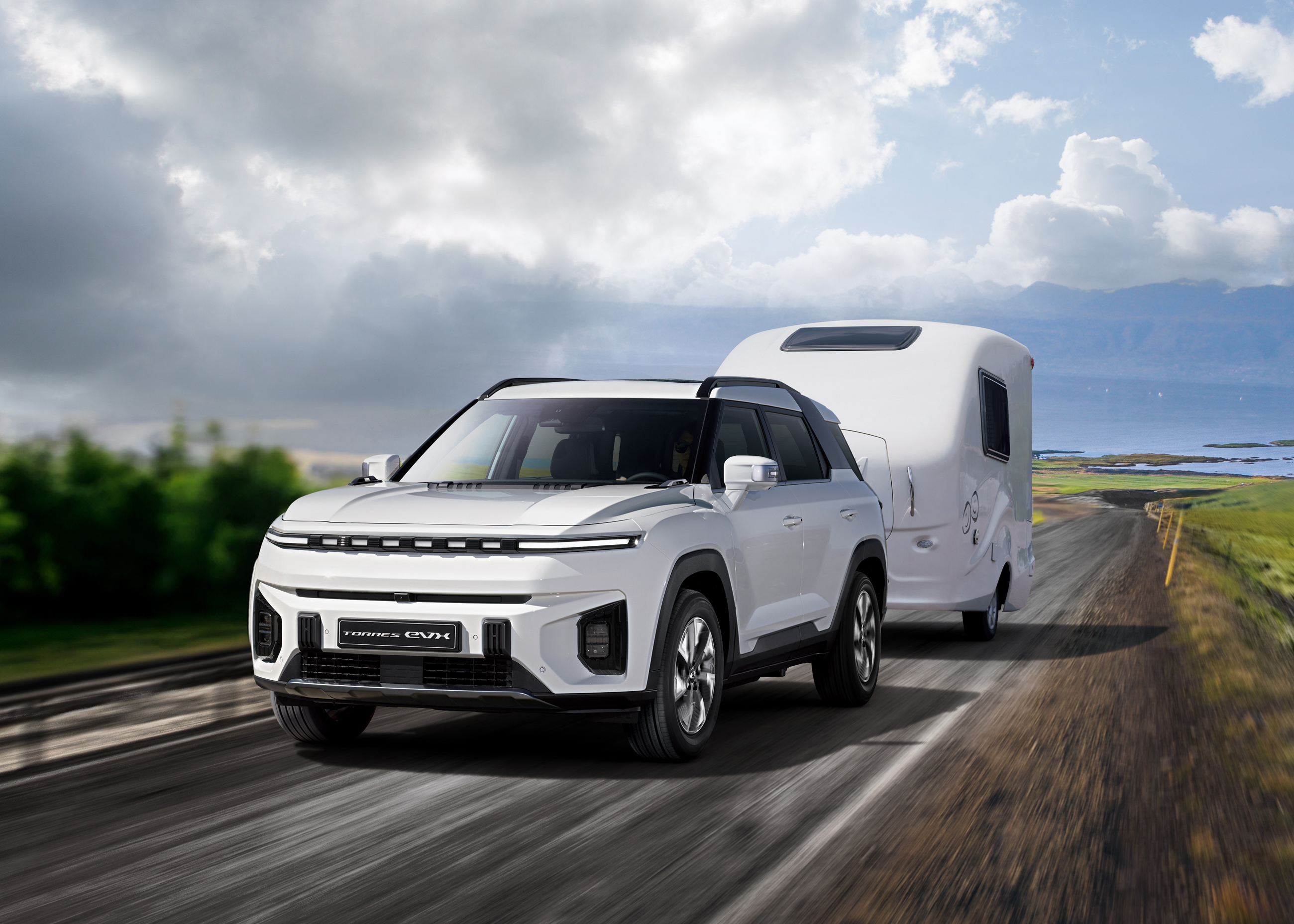
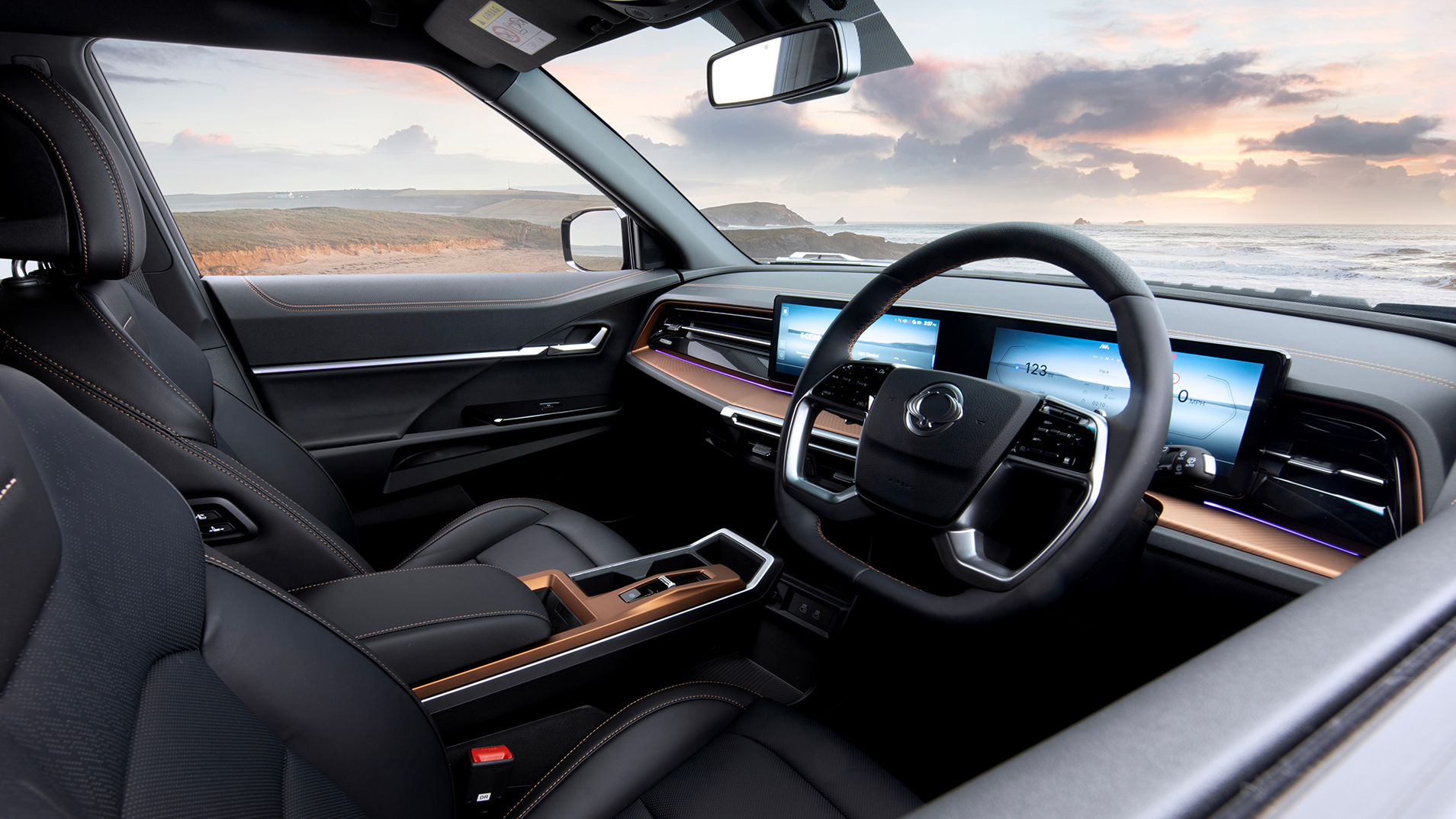


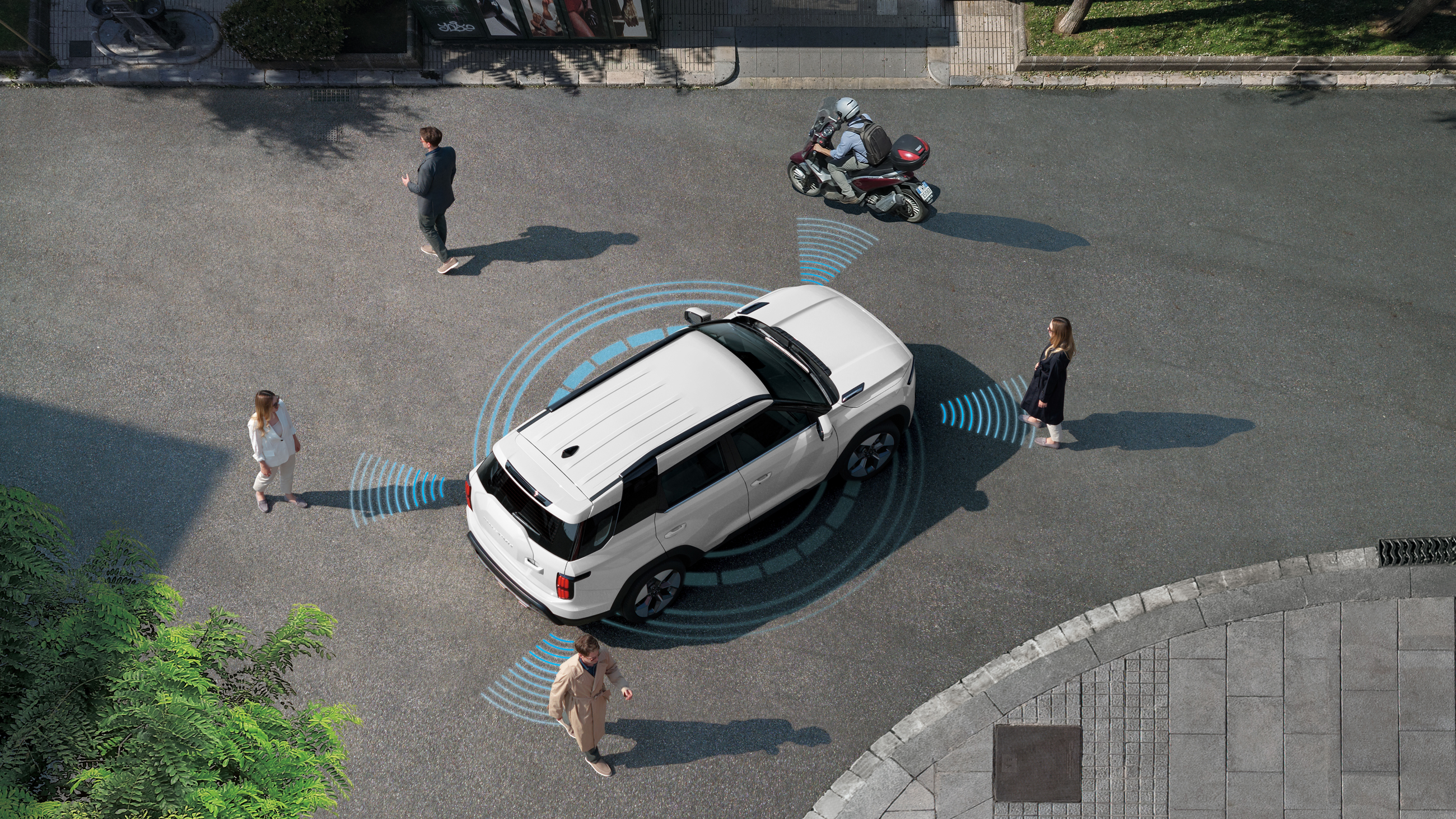







Image /

